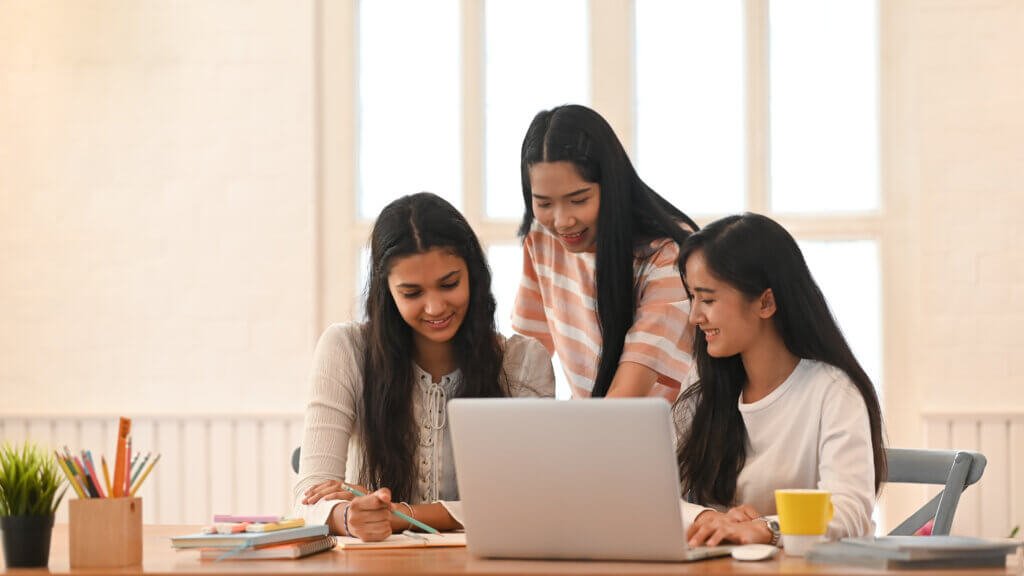
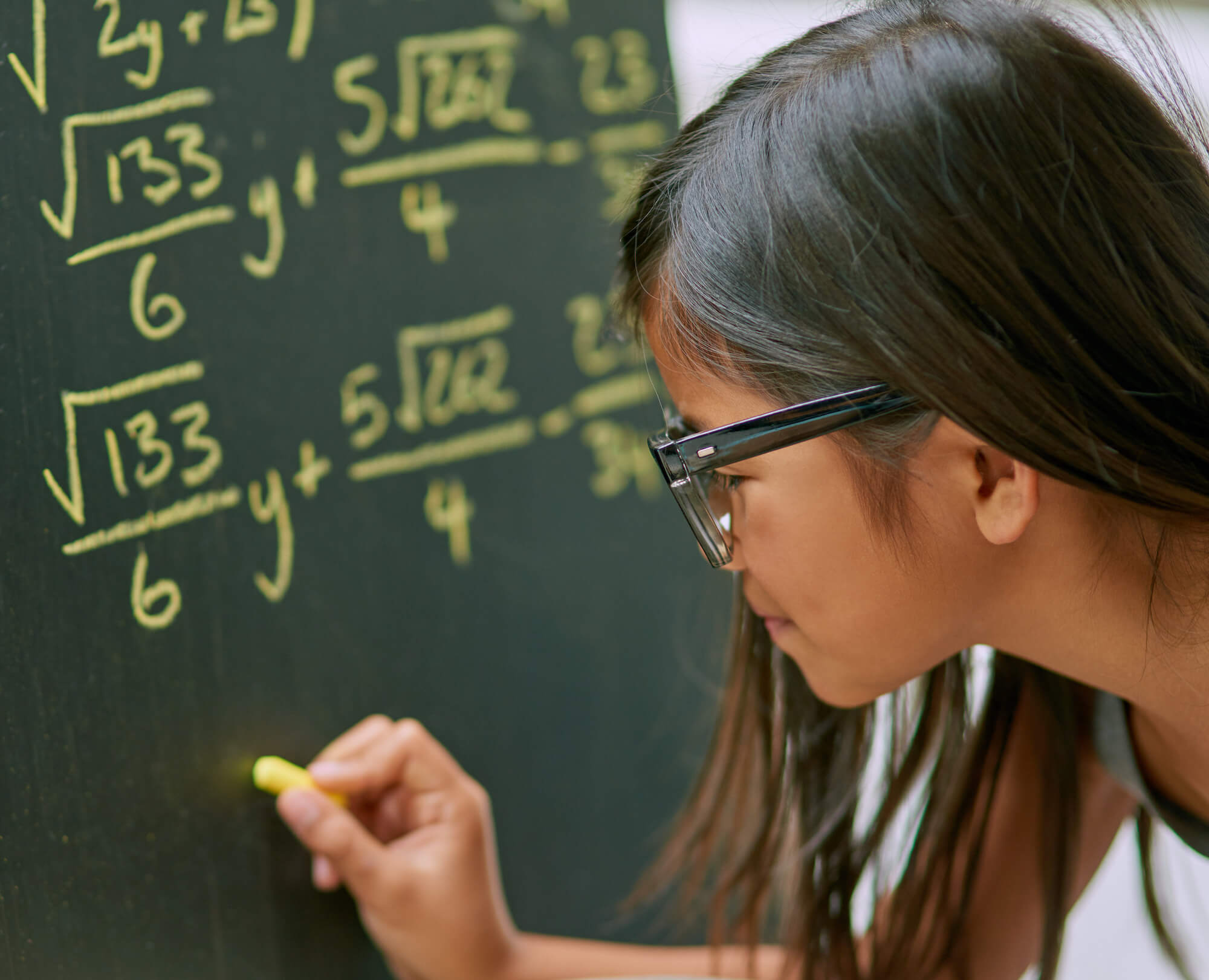

Small group learning has been recognized as an effective educational strategy that fosters a supportive learning environment, encourages active participation, and enhances student outcomes. In the context of competitive exam preparation, such as JEE and NEET, the benefits of small group learning are particularly significant. This article explores how small group learning can impact student success and why it’s a valuable approach for academic excellence.
Understanding Small Group Learning
Small group learning involves dividing students into smaller groups where they can interact more closely with their peers and instructors. This setting allows for more personalized instruction, collaborative learning, and immediate feedback, making it a powerful tool for academic success.
Key Benefits of Small Group Learning
- Personalized Attention: In smaller groups, instructors can give more individualized attention to each student. This personalized approach helps identify and address specific learning needs, ensuring that no student is left behind. It also allows teachers to tailor their teaching methods to suit the learning styles of each student.
- Enhanced Participation: Small group settings encourage active participation. Students are more likely to engage in discussions, ask questions, and share their thoughts without the intimidation that often comes with larger classrooms. This active involvement enhances understanding and retention of the material.
- Collaborative Learning: Learning in small groups promotes collaboration among students. They can work together on problems, share different perspectives, and learn from each other’s strengths. This collaborative environment fosters a sense of community and support, which is beneficial for academic and social development.
- Immediate Feedback: With fewer students to manage, instructors can provide immediate feedback on assignments and assessments. This timely feedback helps students understand their mistakes and learn from them quickly, improving their overall performance.
- Development of Critical Thinking Skills: Small group learning often involves problem-solving activities and discussions that stimulate critical thinking. Students learn to analyze problems, consider various solutions, and make informed decisions, which are essential skills for competitive exams like JEE and NEET.
- Increased Confidence: The supportive environment of a small group helps build student confidence. As students become more comfortable expressing their ideas and answering questions, their self-esteem grows, positively impacting their academic performance.
- Adaptability and Flexibility: Small group learning offers the flexibility to adapt lessons based on the group’s progress and needs. Instructors can adjust the pace and focus of the lessons, ensuring that all students understand the concepts thoroughly before moving on.
- Strengthened Teacher-Student Relationships: Closer interaction in small groups helps build stronger relationships between teachers and students. This rapport can enhance student motivation and trust, leading to a more productive and enjoyable learning experience.
The ConnectEd Advantage
At ConnectEd, we understand the profound impact that small group learning can have on student success. Our Foundation Program is designed to leverage the benefits of small group learning to help students in grades 9 and 10 prepare effectively for competitive exams like JEE and NEET.
Our program maintains small batch sizes to ensure personalized attention and a supportive learning environment. Expert tutors provide tailored instruction, regular assessments, and immediate feedback, helping each student achieve their full potential. The collaborative atmosphere fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills, essential for excelling in competitive exams.
By choosing ConnectEd’s Foundation Program, you’re giving your child the advantage of a learning environment that prioritizes their individual needs and academic growth. Our commitment to small group learning ensures that every student receives the attention, support, and resources they need to succeed.
For more information, visit our Foundation Program page or contact us at hello@learnconnected.in. Together, we can help your child achieve their academic goals and excel in competitive exams.
blog & news
Stay Informed, Stay Inspired.

The Interconnected Nature of Science: Why Your Child Needs Strong Fundamentals in Both Physics and Chemistry

CBSE Class 11 vs. Class 12: What Changes and How Your Child Should Adapt Their Study Strategy
Start your journey
with ConnectEd.

Start your journey
with ConnectEd.

Get in touch with us with any inquiries or assistance.
ADDRESS
Visit us for a personal consultation or meeting.